Heat Integration of the Haber-Bosh process for the production of green ammonia
Abstract
Ammonia is an important compound in the agricultural industry due to its large application in nitrogen-based fertilisers. The most common ammonia production pathway is the Haber Bosch process, in which hydrogen from natural gas and nitrogen react. As natural gas prices keep rising and the decarbonisation of the chemical industry is required, it is important to start implementing large-scale green ammonia production processes [1].
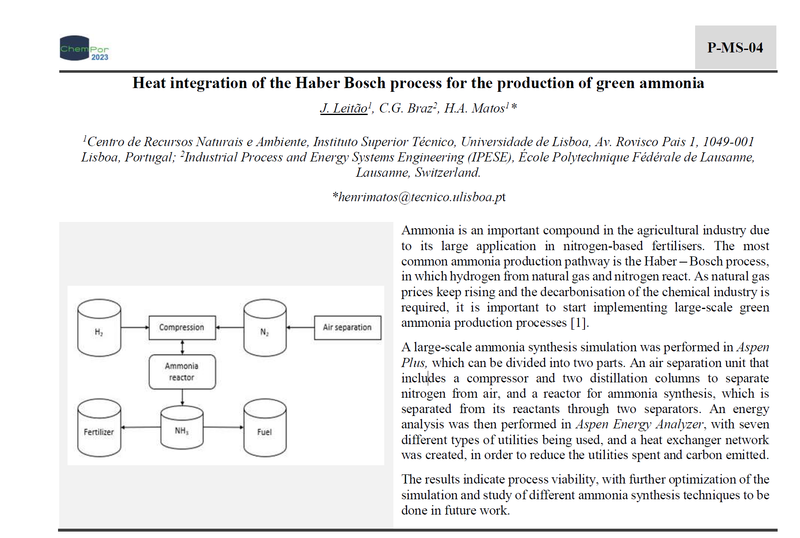
A large-scale ammonia synthesis simulation was performed in Aspen Plus, which can be divided into two parts. An air separation unit that includes a compressor and two distillation columns to separate nitrogen from air, and a reactor for ammonia synthesis, which is separated from its reactants through two separators. An energy analysis was then performed in Aspen Energy Analyzer, with seven different types of utilities being used, and a heat exchanger network was created, in order to reduce the utilities spent and carbon emitted.
The results indicate process viability, with further optimization of the simulation and study of different ammonia synthesis techniques to be done in future work.